
Research importance
CHARACTERIZATION OF THE DNA COMPOUND AT THE QUANTUM MECHANICAL LEVEL: from a molecular standpoint, the DNA molecule is huge, preventing the application of any quantum mechanical method, even with the current computational technology, for its investigation. Nevertheless, if we visualize the DNA as a polymer constituted by small basic units (the 4 nucleic acid bases (NABs)), then it is possible to study the DNA by segments with the use of quantum physics. The goal of this research is the proper understanding of our life origins.
Contribution to the research
WE HAVE PERFORMED A DETAILED AND SYSTEMATIC INVESTIGATION of different DNA building blocks like the nucleic acid bases, Watson-Crick pairs and mini-sequences of the nucleic bases. Their structural and electronic properties are correlated with the DNA stability and biochemical activity. For instance, based on the molecular electrostatic potentials, we have concluded on the existence of a variety of H-bonded pairs, different to the common Watson-Crick pairs. Experiments on DNA derivatives confirm different pairing among DNA compounds. In the pairing process, the electronic charge is reaccomodated at the interaction region between fragments, inducing local polarization, and producing the lost of some chemical binding sites. On the other hand, a stacking configuration of the NABs shows little charge redistribution, uncapable of altering the molecular electrostatic potentials of the sugar and phosphate subunits. Thus, the recognition of DNA segments (or the selectivity in the interactions of DNA with other compounds) proceeds at relatively short distances as a result of a poor influence of NABs on the DNA structural backbone. We have calculated the harmonic vibrational spectra of nucleic acid bases in the frame of density functional theory (DFT). The results show good agreement with experiments. The calculations provided assignments for IR, Raman, and neutron inelastic scattering spectroscopies. The vibrations constitute fingerprints of each compound for its identification in larger systems. General vibrational trends of the single and paired NABs were observed, as family fingerprints. Contrary to the single NABs, the Watson-Crick pairs additionally exhibit characteristic vibrations associated to the hydrogen bridges. Concurrently, we were able to determine the performance of several DFT approximations to exchange-correlation functionals. For H-bonded systems (a binding different to the covalent bond) the use of the exchange-correlation functional are critical and care should be excersized. The computation of binding, zero-point, reorganization, interaction and hydrogen-bond energies, dipole moments, rotational constants and atomic populations has been also done, and correlated with the stability and properties of the DNA. It is observed that the hydrogens that participate in the binding of NABs not only ensure a weak linking between compounds, but also it is the molecular way to preserve the electronic identity of each NAB integrated in the DNA complex. Features like a weak bonding make possible the process of exact duplication of the DNA chain, while the preservation of the electronic identity of NABs in the DNA polymer makes possible the saving and accurate interpretation of the genetic information.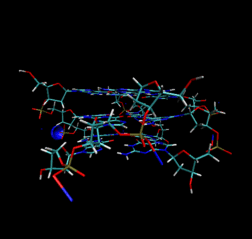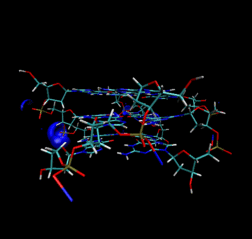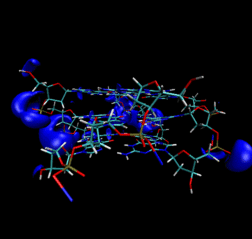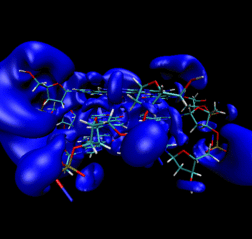
Benefits for the Scientific Community and Society
OUR WORK ON STRUCTURAL AND ENERGETIC ASPECTS OF DNA BASES has contributed to understand the stability, flexibility and reactivity of the DNA compound of concern in the formation of DNA and to characterize the type of interactions in which DNA can engage, like selection and mutation processes. On the other hand, the vibrational spectra may be of help in genetics for the fast identification of nucleotides embedded in large biocompounds. The frequencies and normal vibration modes might be also taken as reference data to determine the magnitude and direction of environmental forces capable of spectral manifestation. From a theoretical point of view, the vibrations are useful for the parameterization of force fields. This knowledge is important for the molecular design of drugs, in principle capable to cure genetic diseases with minimal side effects.
Future projection
IT IS OUR AIM TO CONTINUE WITH OUR STUDY OF DNA AT THE QUANTUM MECHANICAL LEVEL. We are presently interested on the dynamical role that DNA plays in a variety of specific interactions with proteins. We believe it is also important to establish the effects of dangerous metals on the structure and electronic properties of the nucleic acid bases. From the macroscopic point of view, it is well known that metals are capable to lead to metabolic problems in the host. Such problems start at the microscopic level, when the metals locally alter and even disrupt the genetic code.
My articles in this field
Structural and electronic property changes of the nucleic acid bases upon base pair formationR. Santamaria, A. Vazquez
Jour. Compt. Chem. 15 , 981-996 (1994)
Structures and energetic properties of B-DNA nucleotides
R. Santamaria, A. Quiroz-Gutierrez, C. Juarez
Jour. Molec. Struct. (Theochem) 357 , 161-170 (1995)
Molecular electrostatic potentials and mulliken charge populations of DNA mini-sequences
R. Santamaria, G. Cocho, L. Corona, E. Gonzalez
Chem. Phys. 227 , 317-329 (1998)
Vibrational spectra of the nucleic acid bases and their Watson-Crick pair complexes
R. Santamaria, E. Charro, A. Zacarias, M. Castro
Jour. Comput. Chem. 20, 511-530 (1999)
Structural and electronic changes of cytosine upon addition of atomic sulfur
P. Mollinedo-Rosado, R. Santamaria
Jour. Molec. Structure (Theochem) 805 , 111-117 (2007)
Vibrational circular dichroism and IR absorption spectra of amino acids: a density functional study
Zhi Ji, R. Santamaria, I. L. Garzon
Jour. Phys. Chem. A114, 35913601 (2010)
Reactivity of a model tetraplex from a molecular electrostatic potential and an HOMO-LUMO energy gap study
J. A. Mondragon-Sanchez, R. Santamaria, Ramon Garduno Juarez
submitted 2010
Gallery
IMAGES AND ANIMATIONS are presented in the gallery to illustrate some of my research results. Selected movies from the web are embedded to also illustrate the key role that DNA assumes in a variety of complex biochemical processes (embedded movies).










