Diffusing wave Spectroscopy (DWS) is a relatively new technique that extends the standard dynamic light scattering technique to the multiple scattering regime. Here, the  transport of light after some penetration given by l*, can be approximated with a diffusive theory. For this, we need that the sample has a milky like opacity that can be obtained adding probe particles to the fluid under study.
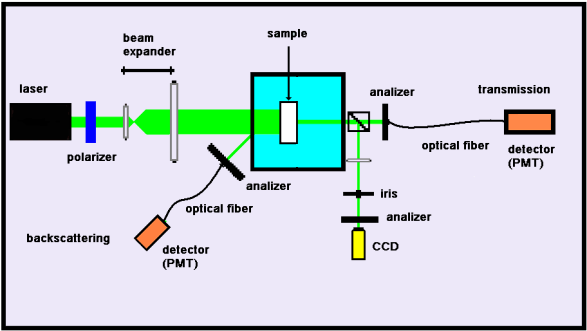
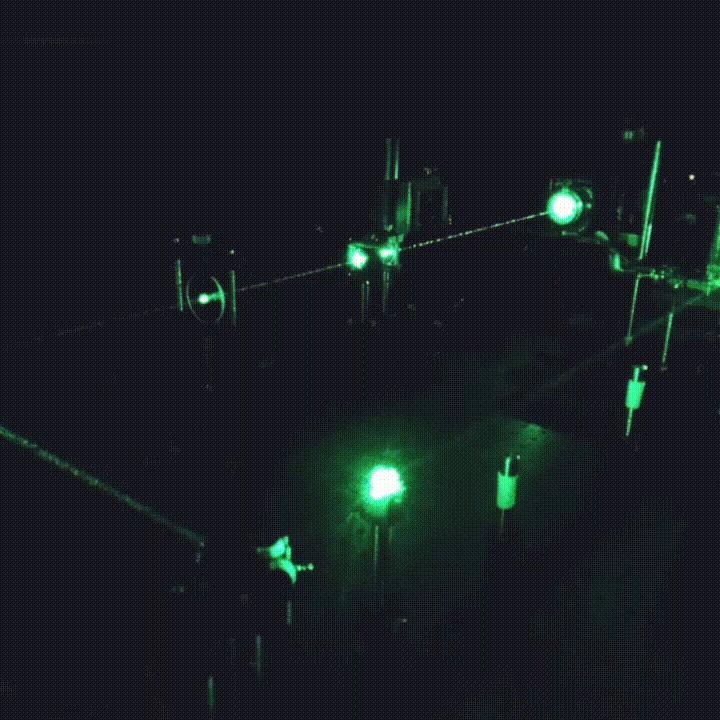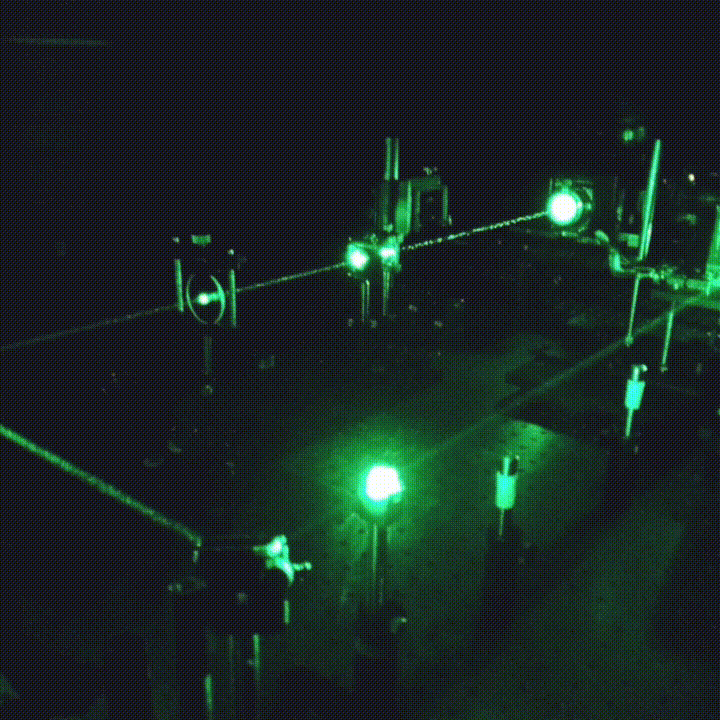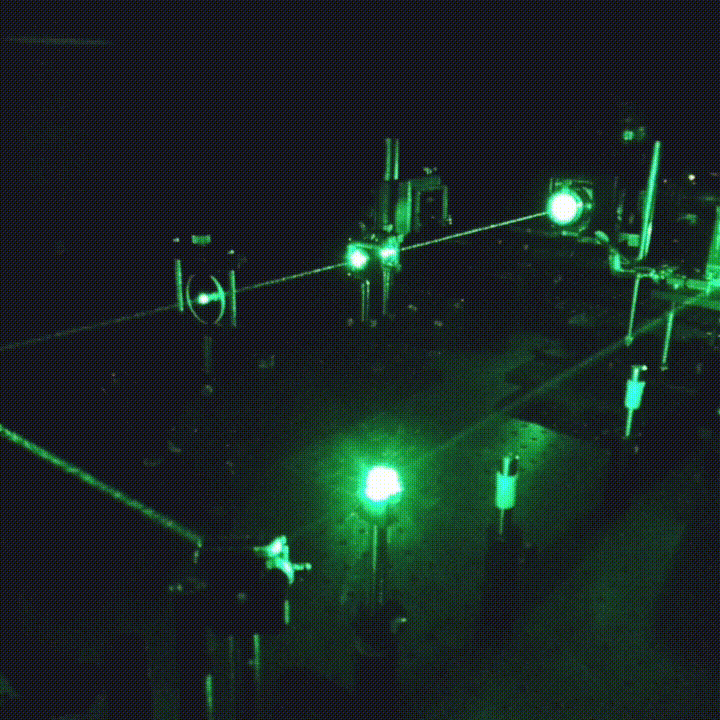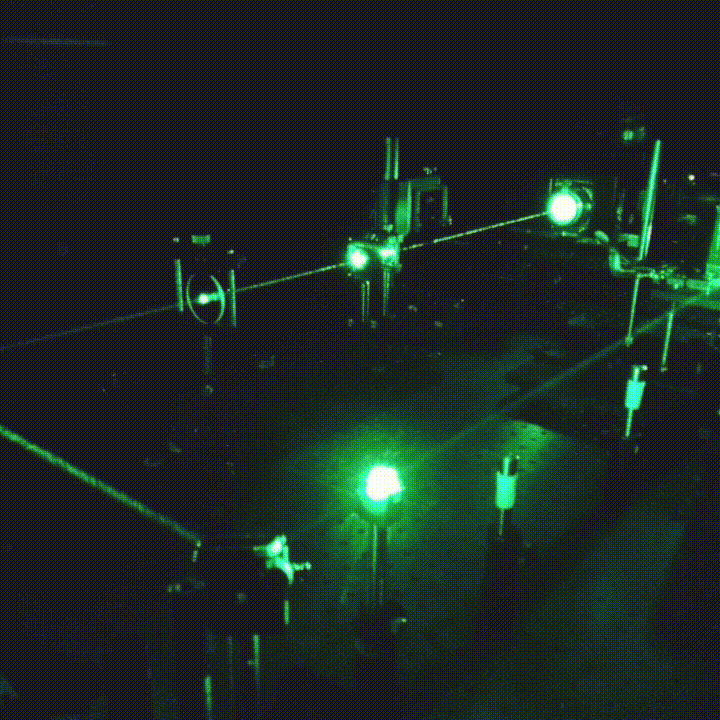
The experimental setup is shown below. A laser beam is expanded to a diameter of ca. 1.0 cm before it enters the sample. The detection of the scattered light is made almost with the same setup as in the standard dynamic light scattering (photomultiplier tube, preamplifier, correlator, etc).
With this technique, we can measure the mean square displacement (msd) of the probe particles on scales as low as tenths of nanometers. Also, we can use this msd to obtain the microrheology for the system under study; in particular G'(w) and G''(w)
 |
 |
 |

 Overbeck/L2phase transition in the C
21monolayer
Overbeck/L2phase transition in the C
21monolayer