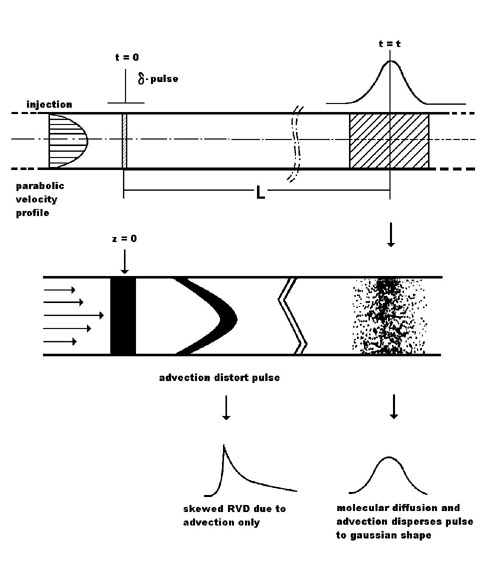
The Taylor dispersion technique is based on the spreading, by the joint action of convection and molecular diffusion, of an injected binary-mixture pulse in a laminar flowing stream of the same mixture at slightly different composition. Under adequate conditions, the pulse concentration profile will eventually become Gaussian, and the center of gravity of the profile will move with the mean velocity of the laminar flow. The theory for the development of an ideal equipment to measure mutual diffusion coefficients using this method was revised by Alizadeh et al. Furthermore, they presented detailed criteria for the design of a practical instrument for measuring mutual diffusion coefficients. The principle of operation of the instrument is presented in the figure.

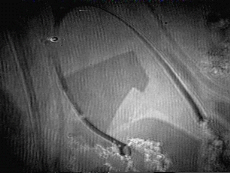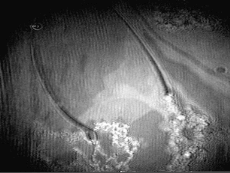 Overbeck/L2phase transition in the C
21monolayer
Overbeck/L2phase transition in the C
21monolayer