

HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL AUTONOMA DE MEXICO
|
| PRECISION ANALYSIS OF THE ELECTROWEAK STANDARD MODEL. LATEST RESULTS the main aim of this section is to show a summarize of the data analysis. The data allow a simultaneous determination of MH, mt, sin2 &thetaW, and the strong coupling &alphas(MZ). The global fit to all data, including the CDF/D0 average, mt = 172.7 ± 3.0 GeV, yields
MH=89+38-28 GeV, We used GAPP (Global Analysis of Particle Properties) for the first time for the 1997 off-year partial update of our contribution to the Particle Data Group in C. Caso et al, Eur. Phys. J. C3, 1 (1998). Important updates can be found in hep-ph/9809352 and in D.E. Groom et al, Eur. Phys. J. C15, 1 (2000). The Figure 1 below represents the status of the Standard Model. 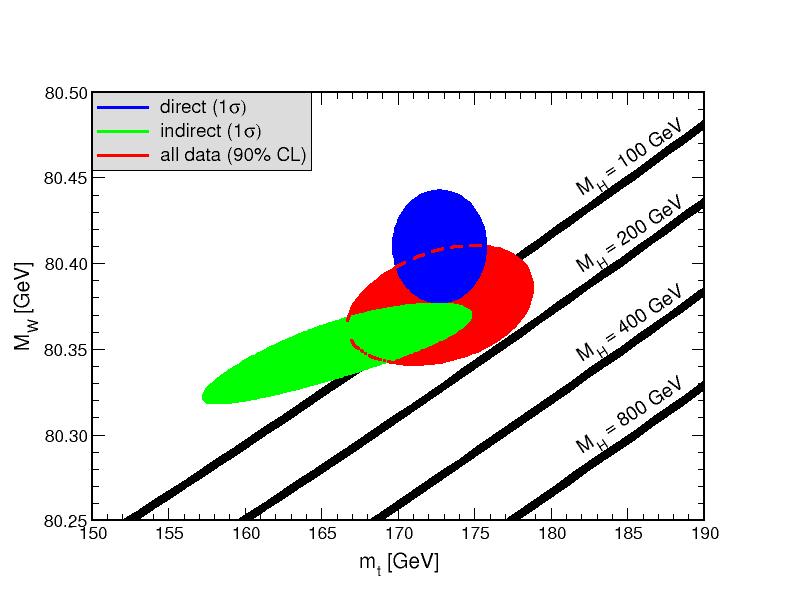
Figura 1. One standard deviation (39.35 %) uncertaities in MH as a funtion of mt for the direct and indirect data, and the 90% CL region (Δχ2 = 4.605) allowed by all data. The SM prediction as a funtion of MH is also indicated. The widths of the MH bands reflect the theoretical uncertainty from α(MZ). The most important result within the SM is presently the extraction of the Higgs boson mass, and the resulting limits at 95 (90, 99)% confidence upper limit are MH < 194 (176, 235) GeV respectively. The extracted MH is strongly correlated with mt as can be seen in the next figure, which shows the one standard deviation contours for the lineshape variables and cross section ratios, the Z pole asymmetries, deep inelastic neutrino scattering, MW, the direct mt constraint, and the 90% CL allowed region by all data. 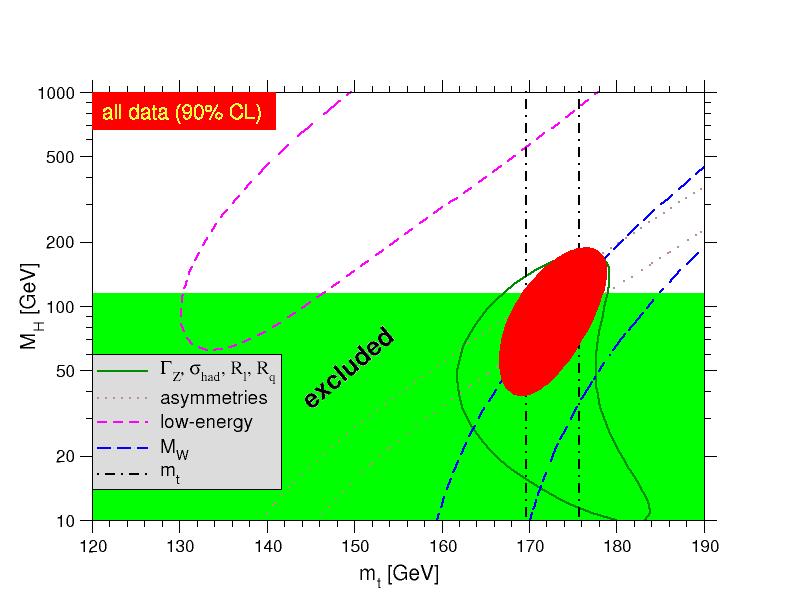
Figure 2. One-standard-deviation (39.35%) uncertainties in M
H as a funtion of mt for various inputs, and the 90% CL region
(Δχ2=4.605) allowed by all data. &alpha(MZ)=0.120
is assumed except for the fits including the Z-lineshape data. The 95% direct lower limit
from LEP 2 is also known. GAPP was also essential in a study of Bounds on Supersymmetry from Electroweak Precision Analysis, in collaboration with Damien Pierce, published in Nucl. Phys. B526, 53 (1998). Within the frameworks of supergravity and gauge mediated supersymmetry breaking we systematically investigated the allowed parameter spaces in these classes of models. Precision observables, direct limits on superparticles, as well as electroweak and unification scale boundary conditions, have all been considered simultaneously. New limits on superpartners and extra Higgs scalars could be set. For results on extra Z bosons, see our paper Constraints on Extended Neutral Gauge Structures, Phys. Lett. B456, 68 (1999). As for a more model independent parametrization of new physics we show the current constraints on the oblique parameters, S and T (with U = 0), in the following figure. The one standard deviation contours for the individual data sets are for a reference Higgs boson mass of 117 GeV. For the fits to all data we show the 90% CL contours. 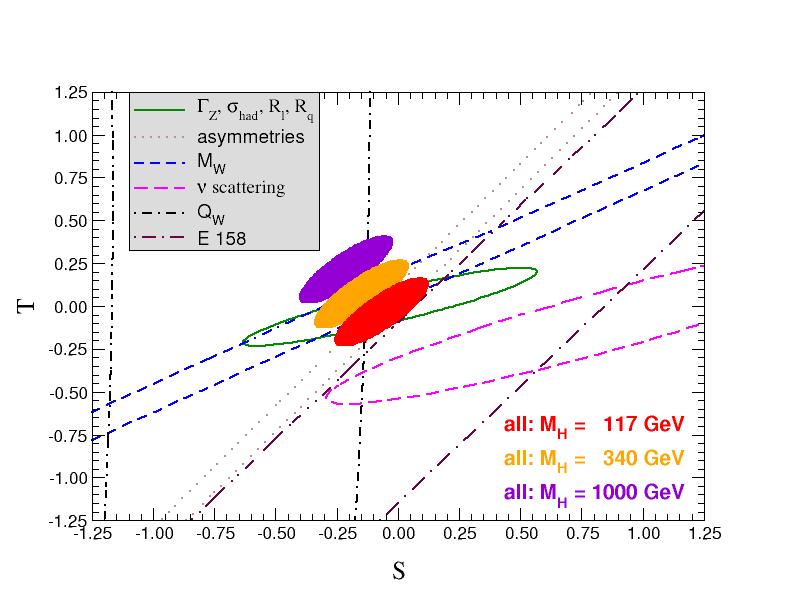
Figure 3. 1 σ constraints (39.35%) on S and T from various inputs combined with MZ. S and T represent the contributions of new physics only. (Uncertainties from mt are included in the errors.) The contours assume MH = 117 GeV except for the central and upper 90% CL contours allowed by all data, which are for MH= 340 GeV and 1000 GeV, respectively. Data sets not involving MW are insensitive to U. Due to higher order effects, however, U=0 has to be assumed in all fits. αs is constrained using the τ lifetime as additional input in all fits. |

| Jens ErlerInstituto de Fisica-UNAMe-mail: erler@fisica.unam.mx | Paul LangackerDepartment of Physics, University of Pennsylvaniae-mail: pgl@electroweak.hep.upenn.edu | Marcial SanchezInstituto de Fisica - UNAMe-mail: mar@fisica.unam.mx | ||||